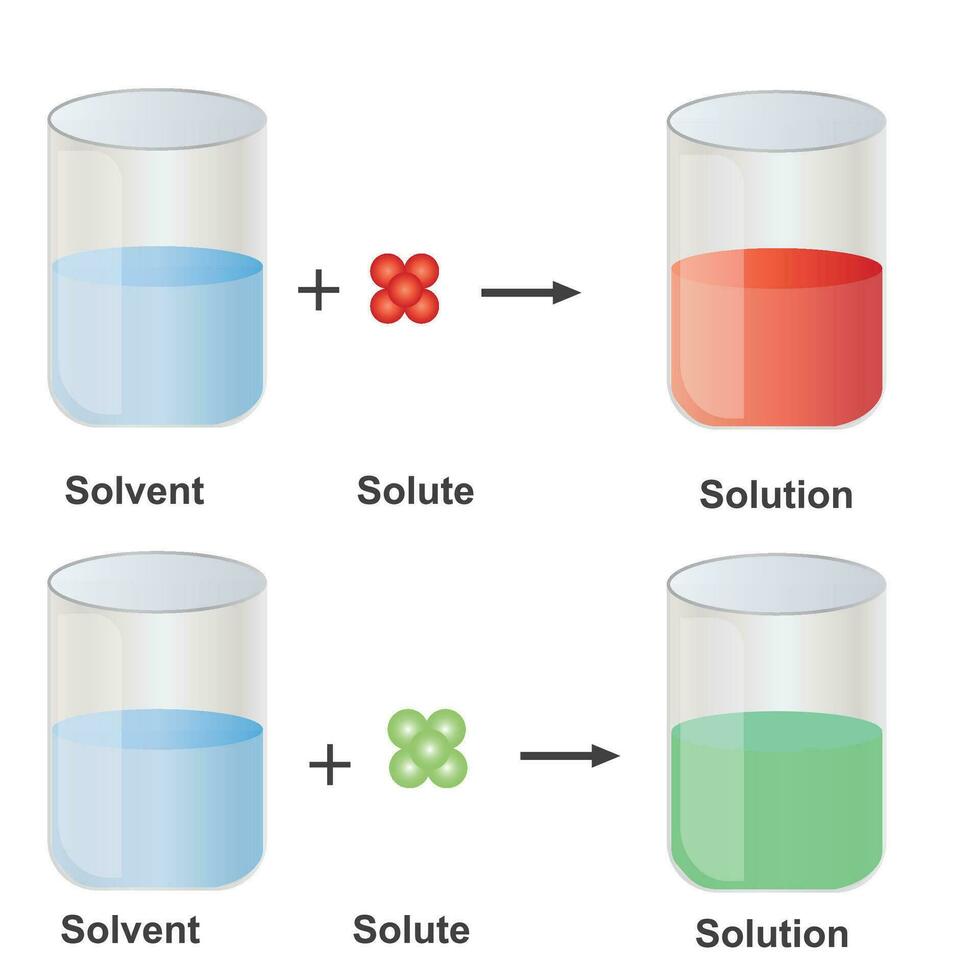
In Forming A Solution The Solute Always - When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. In forming a solution, the solute always: Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. What causes a solution to form?
What causes a solution to form? A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. In forming a solution, the solute always: The simple answer is that the solvent and the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the.
What causes a solution to form? In forming a solution, the solute always: A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.
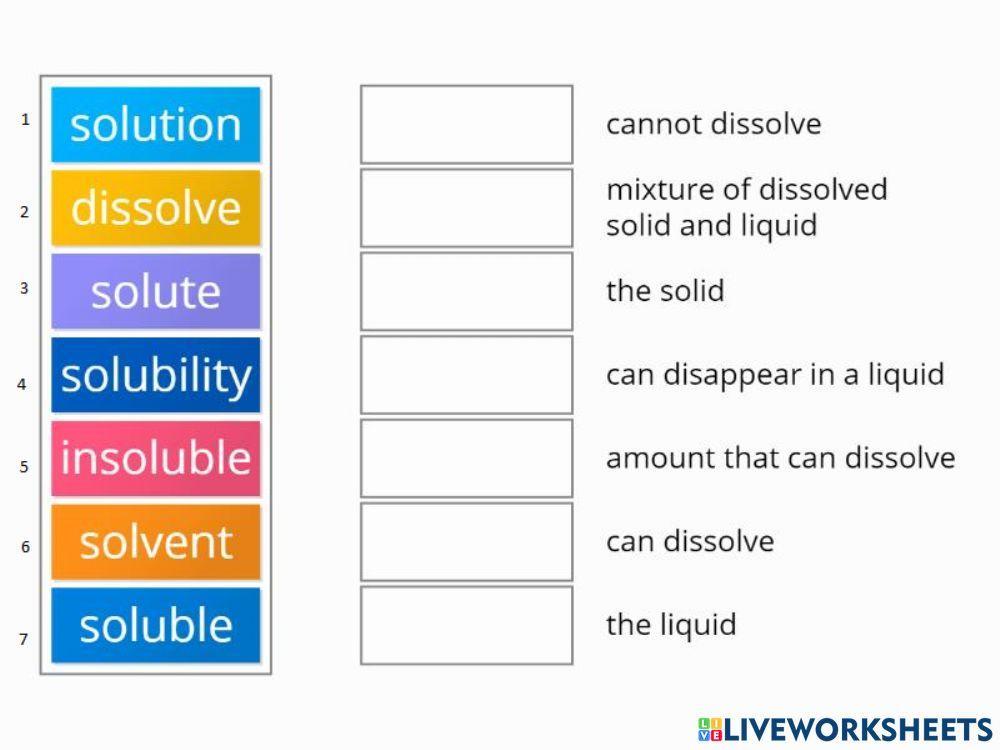
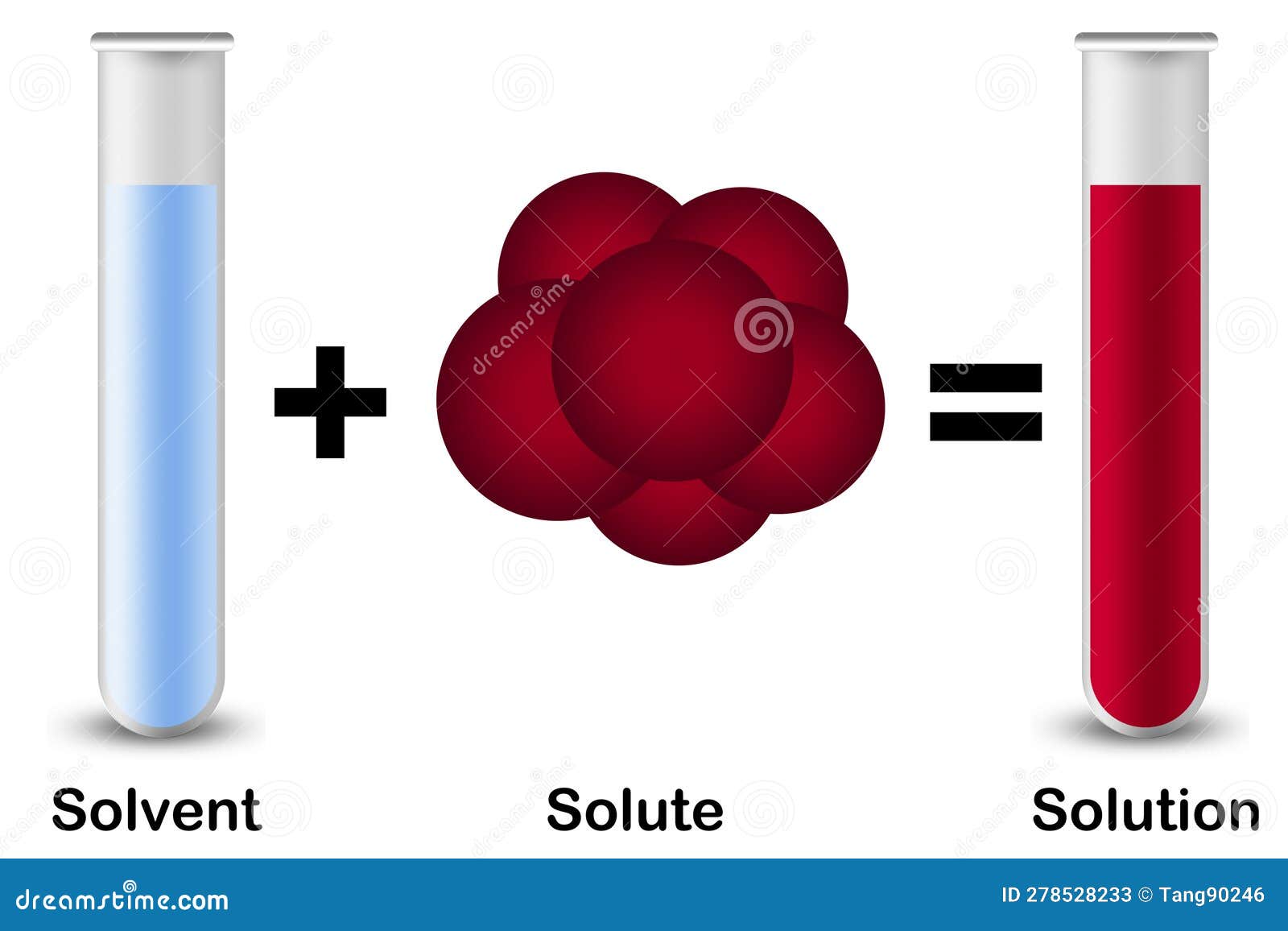
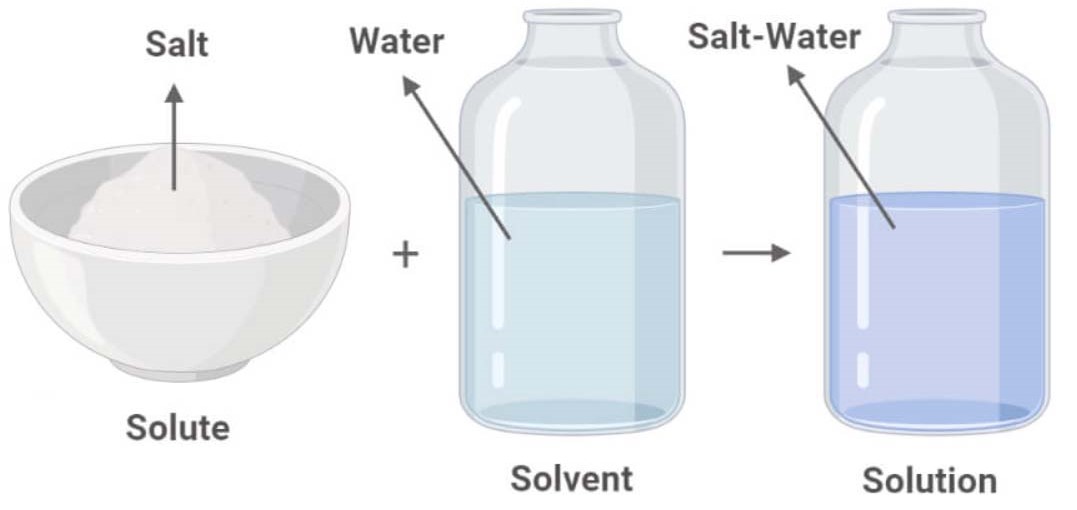
Solutions. Solubility homogeneous mixture. Solute, solvent and solution
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. What causes a solution to form? In forming a solution, the solute always: When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the.
Solute and Solvent Combinations — Overview & Examples Expii
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent.
Solute In Science
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. In forming a solution, the solute always: When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak.
Examples Of Solute, Solvent And Solution Examples Of Solute, 44 OFF
A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. In forming a solution, the solute always: In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.
Difference Between Solvent and Solute Definition, Properties, Examples
A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. In forming a solution, the solute always: What causes a solution to form?
Solute, Solvent and Solution Isolated with Red Solute Stock
When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. What causes a solution to form? In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak.
Solute Energy Education
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. The simple answer is that the solvent and the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak.
Understanding the Solute and Solvent Relationship
When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. What causes a solution to form? The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
In a solution, is the solute always a solid.
The simple answer is that the solvent and the. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. In forming a solution, the solute always: Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. What causes a solution to form?
Solute vs. Solvent 5 Key Differences, Pros & Cons, Examples
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. What causes a solution to form? A strong electrolyte always forms a very concentrated solution and a weak. Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates. In forming a solution, the solute always:
A Strong Electrolyte Always Forms A Very Concentrated Solution And A Weak.
In order to form a solution, the solute must be surrounded, or solvated, by the solvent. When a solute dissolves in a solvent, its particles separate and disperse uniformly throughout the. What causes a solution to form? The simple answer is that the solvent and the.
In Forming A Solution, The Solute Always:
Dissolves dissociates both dissolves and dissociates.